The NCERT Full Form is “National Council of Educational Research and Training”. NCERT holds significant importance in the education scenario because of its multifaceted contribution which positively influences education policies, curriculum development, teaching methods and learning resources. It serves as a premier organization that strives to enhance the overall quality of education in various countries.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Importance of NCERT in Education Scenario:
- Curriculum Development: NCERT plays an important role in developing and revising the national curriculum. By providing expert guidance and standardized framework, it ensures that educational content is relevant, comprehensive and in line with modern educational needs.
- Quality Learning Resources: NCERT creates textbooks, supplementary materials and educational resources that reflect accurate information, encourage critical thinking and promote holistic learning. These resources cater to diverse learning styles and support both teachers and students.
- Teacher Empowerment: NCERT organizes teacher training programmes, workshops and seminars. By enhancing the skills, knowledge and teaching methods of teachers, NCERT contributes to more effective and engaging classroom experiences.
- Educational Research: NCERT conducts research to improve educational practices. Its findings influence the adoption of educational policies, educational strategies and innovative teaching techniques.
- Equity and Inclusion: NCERT focuses on creating inclusive educational content that meets the needs of students from diverse backgrounds and abilities. It contributes to reducing educational inequalities and ensuring access to quality education for all.
- Standardization: NCERT sets educational standards and guidelines that promote consistency and uniformity in curriculum across various fields. This ensures that students receive a comparable education regardless of their location.
- National Educational Goals: The expertise of NCERT contributes to achieving the National Educational Goals by providing insight into effective teaching, learning methodologies and assessment practices.
- Global Collaboration: NCERT collaborates with international educational organizations by sharing best practices and experiences. This global exposure enriches its understanding of educational trends and innovations.
- Educational Policy: NCERT provides valuable inputs to educational policy makers, contributing to evidence-based decisions that shape the direction and effectiveness of the education system.
- Continuous Improvement: NCERT continues to adapt to changing educational needs and technological advancements. It regularly updates its curriculum, resources and strategies to keep education relevant and responsive to emerging challenges.
Importance of understanding the NCERT full form and historical roots of NCERT:

- Clarity of Purpose: Understanding the full form of NCERT clarifies its identity as a comprehensive institution engaged in educational research and training. This knowledge sets the stage for exploring its multifaceted role in the educational field.
- Historical Context: Learning about the historical roots of NCERT provides a contextual understanding of why and how it was established. It helps individuals appreciate the inspirations and challenges that led to its creation.
- Evolution of Educational Philosophy: Going deep into the history of NCERT reveals its evolving educational philosophy. Knowledge of its initial objectives and how they have changed over time provides insight into the changing needs and aspirations of India’s education system.
- Policy Implications: Understanding the historical journey of NCERT allows us to see its impact on educational policies. By studying its involvement in policy making, one can understand how it has shaped the educational direction of the nation.
- Educational Innovations: Historical exploration reveals how NCERT has been at the forefront of educational innovations. This understanding highlights the organization’s commitment to finding effective teaching and learning strategies.
- Catalyst for Change: The history of NCERT has often reflected the educational, social and technological changes that have taken place in India. Recognizing how it has adapted to these changes underlines its role as a catalyst of positive change in education.
- Continuity and Growth: Historical insights show the continuity of NCERT’s efforts and its commitment to reform education over the decades. This continuity adds to its credibility as an enduring institution dedicated to education.
Decoding the NCERT Full form
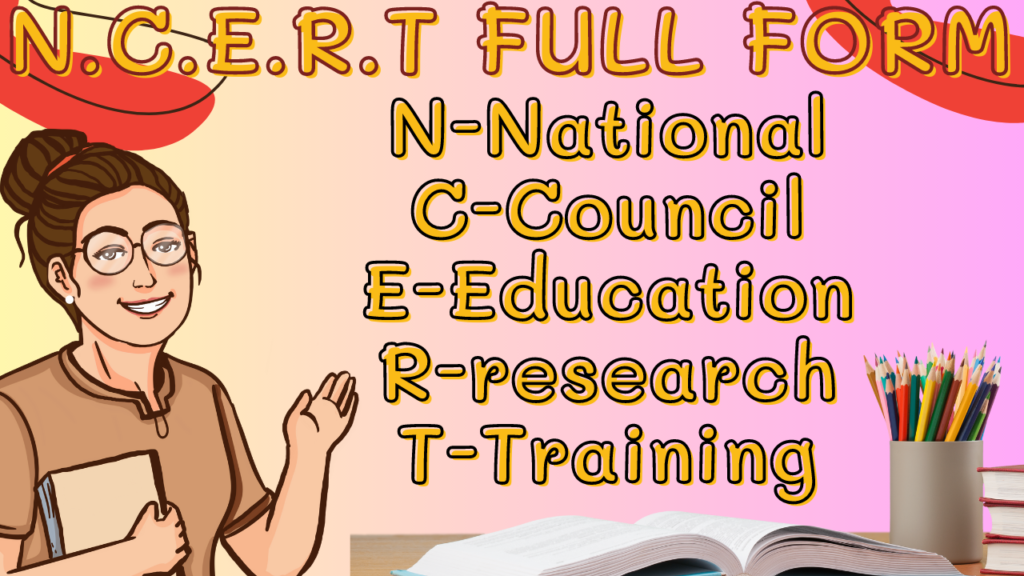
The abbreviation “NCERT” stands for “National Council of Educational Research and Training”. Each word in this acronym holds a significant meaning which collectively highlights the multifaceted and important role of the organization in shaping education.
- National: The word “national” indicates that NCERT works at a nationwide level, affecting education throughout the country. This reflects the organization’s role as a central authority that influences educational policies, standards and practices at the national level. NCERT’s initiatives and resources are designed to meet the diverse needs of students and teachers from different states and regions.
- Council: The term “council” refers to an authoritative and governing body that is responsible for making informed decisions and setting guidelines. NCERT acts as an advisory and regulatory council in the field of education, providing expert guidance on matters relating to curriculum, pedagogy and educational research. It plays an important role in shaping educational policies and practices through its recommendations and expertise.
- Educational: The word “Educational” underlines the primary focus of NCERT: education in all its dimensions. NCERT is dedicated to enhancing the quality of education by developing curriculum framework, educational resources and research-based approach that promote holistic learning. Its contribution extends to curriculum development, teacher training, educational research and creation of effective teaching materials.
- Research: The word “research” emphasizes NCERT’s commitment to evidence-based practices. Research is an integral part of the organization’s approach, as it continually studies educational trends, learning methodologies, and educational innovations. By undertaking research, NCERT contributes to the advancement of educational strategies and ensures that its initiatives are rooted in best practices.
- Training: The term “Training” highlights the role of NCERT in enhancing the capabilities of teachers. The organization provides teachers with comprehensive training programs, workshops, and resources, equipping them with updated teaching methods, technical skills, and effective classroom management techniques. It empowers teachers to provide high quality education and engage students effectively.
Tracing the Historical Origins of NCERT
The history of National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) is a story of visionary vision and quest for a sound education system. Established in the backdrop of post-independence India, the foundation of NCERT was laid with an aim to change the educational landscape of the country and shape the minds of its future generations.
Establishment of NCERT: A Glimpse of its Historical Context and Founding Inspirations

Historical Context
The middle of the 20th century was a defining era for India. With the dawn of independence in 1947, the country embarked on a journey of self-discovery and development. Education, seen as the cornerstone of progress, was recognized as a powerful tool for promoting social, economic and cultural development. However, the existing educational practices were diverse and lacked a cohesive framework that could meet the needs of a rapidly developing nation.
Inspirations behind the creation:
The establishment of NCERT in 1961 was a response to these vital needs and aspirations. Several key inspirations led to its creation:
- Curriculum Standardization: The need for a standardized curriculum was evident. Different regions and states adopted different educational approaches, leading to disparities in the quality of education. NCERT’s vision was to develop a unified curriculum that would ensure consistent educational content and opportunities for students across the country.
- Research-Based Pedagogy: The leaders of the time recognized the importance of research-driven educational practices. NCERT was established to conduct rigorous educational research that would inform teaching methods, improve learning outcomes and enhance the quality of education in schools.
- Equity and Access: Inclusive education was a major concern. The goal of the founders of NCERT was to create educational material that catered to the diverse needs of students, regardless of their socio-economic background, linguistic preferences or geographical locations.
- Modernization of Education: As India moved towards industrialization and modernization, the education system needed to be developed accordingly. The objective of NCERT was to provide teachers and students with the necessary tools and resources to keep up with the changing times while preserving the essence of the country’s rich cultural heritage.
- Policy making: The NCERT was conceived as an advisory body to provide expert guidance to the government on matters relating to education. Its research and insights will contribute to informed policy decisions that will shape the future of education in India.
Key milestones and developments Of NCERT
I have given a list of key milestones and developments in NCERT’s journey from its inception to the present day
- 1961 – Establishment: NCERT was established on September 1, 1961 by the Government of India. It started its journey with the mission of conducting educational research and developing curriculum framework for school education.
- 1964 – First Curriculum: The NCERT developed its first National Curriculum Framework, providing guidelines for school education across the country. This is an important step towards standardization of educational material.
- 1970s – Textbook Development: NCERT started making textbooks in line with its curriculum framework. These textbooks quickly gained popularity due to their precise content and innovative teaching methods.
- 1980s – Educational Technology: NCERT embraced the use of educational technology by producing audio-visual materials and introducing computers into the learning process. This demonstrated the organization’s commitment to being at the forefront of educational advancement.
- 1990s – National focus on quality education: During this period, the role of NCERT became even more important as India focused on improving the quality of education. The organization has intensified efforts in curriculum reform, teacher training, and educational research.
- 2005 – National Curriculum Framework: NCERT released a revised National Curriculum Framework (NCF) with emphasis on learner-centred approach, holistic development and integration of knowledge across subjects.
- 2010s – Digital Initiatives: NCERT expanded its digital footprint by launching online platforms for e-learning, educational resources and teacher training. The move reflects the changing educational scenario in the digital age.
- 2016 – Evaluation Reforms: NCERT played a significant role in bringing changes in evaluation practices. It advocated a shift towards conceptual understanding rather than rote memorization, which led to a change in the examination pattern.
- Present – Inclusive Education and Diverse Education: NCERT continues to focus on inclusive education by meeting the diverse learning needs of the students. Its initiatives now include areas such as gender sensitivity, special education and ensuring education for all.
- Ongoing – Policy Impact and Research: NCERT plays an active role in advising the government on educational policies. It conducts research to address current challenges, such as improving learning outcomes, enhancing teacher effectiveness, and adopting technological advances.
- International Collaboration: In recent years, NCERT has increased its collaboration with international educational organizations to promote cross-cultural learning experiences and share best practices.
- COVID-19 Response: The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of adaptive learning. NCERT responded swiftly by providing digital resources and guidelines to facilitate distance learning during school closures.
Prominent figures and initiatives that shaped NCERT
Several notable figures and initiatives have played pivotal roles in shaping the evolution of the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT). These individuals and efforts have contributed to NCERT’s growth, influence, and impact on the education landscape in India. Here are some of the key figures and initiatives:

- Dr. D. S. Kothari: Dr. Kothari, the first Chairman of NCERT, was instrumental in shaping its early direction. His vision of a strong educational foundation and research-based approach laid the groundwork for NCERT’s initiatives and contributions.
- Kothari Commission (1964-66): The Education Commission led by Dr. D. S. Kothari, commonly known as the Kothari Commission, played a significant role in shaping NCERT’s objectives and focus areas. The Commission’s recommendations influenced NCERT’s curriculum development and research strategies.
- Prof. Yash Pal: Prof. Yash Pal, a renowned physicist and educationist, served as the Director of NCERT in the 1980s. Under his leadership, NCERT emphasized innovation and technology in education, incorporating audio-visual aids and introducing computers to schools.
- National Curriculum Frameworks (NCFs): The development of National Curriculum Frameworks, beginning with the first NCF in 1975, marked critical milestones in NCERT’s evolution. These frameworks provided guidelines for curriculum development, pedagogical approaches, and educational content.
- Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA): The SSA initiative aimed at universalizing elementary education in India. NCERT’s involvement in developing materials and teacher training for SSA contributed to its mission of inclusive and equitable education.
- Digital Initiatives: With the increasing integration of technology in education, NCERT launched digital platforms, such as the ePathshala and DIKSHA portals. These initiatives made educational resources accessible to students and teachers digitally.
- National Achievement Surveys (NAS): NCERT introduced the NAS to assess the learning outcomes of students across various subjects. This initiative aimed to measure the effectiveness of educational strategies and identify areas for improvement.
- Teacher Training Programs: NCERT’s consistent efforts in providing professional development for teachers through training programs, workshops, and online courses have significantly contributed to enhancing teaching practices and instructional quality.
- Online Resources: In recent years, NCERT’s online resources, including digital textbooks, interactive modules, and video lectures, have transformed the accessibility of quality education, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Collaborations: NCERT’s collaborations with international organizations, universities, and educational bodies have fostered knowledge exchange, innovative practices, and cross-cultural learning experiences.
- Research Initiatives: NCERT’s research studies and publications on educational trends, learning methodologies, and pedagogical innovations have influenced teaching practices and policy decisions.
- Inclusive Education Initiatives: NCERT’s focus on creating materials for students with diverse learning needs, including those with disabilities, showcases its commitment to inclusive education.

Development of curriculum frameworks, textbooks, and teaching materials by NCERT
The National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) has been a driving force in the development of the curriculum framework, textbooks and teaching materials that form the backbone of education in India. These resources have been carefully crafted to provide a structured and effective learning experience for the students while supporting the teachers in imparting quality education. Let us see how NCERT has contributed in each of these areas:
Curriculum Framework:
NCERT plays a vital role in designing and updating the curriculum framework which serves as the guiding documents for educational content and pedagogy. These outlines outline the learning objectives, topics, and skills that students should acquire at various grade levels. The major aspects of the development of the NCERT curriculum framework include:
- Holistic Approach: The NCERT framework lays emphasis on holistic education encompassing cognitive, emotional and social development. The frameworks consider not only subject knowledge but also critical thinking, life skills and values.
- Interdisciplinary Learning: NCERT promotes interdisciplinary learning, encouraging connections between different disciplines to promote a deeper understanding of real-world issues.
- Inclusivity: The framework is designed to be inclusive, meeting the needs of all learners, including those with disabilities and from diverse backgrounds.
Textbook Construction:
NCERT textbooks are famous for their clarity, accuracy and comprehensive coverage of topics. These textbooks are aligned with the curriculum framework of NCERT and provide a structured learning path for the students. The major aspects of NCERT textbook development include:
- Conceptual clarity: NCERT textbooks focus on building a strong conceptual foundation. They emphasize understanding rather than rote memorization, promoting a deep and lasting grasp of the subject matter.
- Real-life applications: Textbooks often include examples and activities that relate to real-life situations, making learning relevant and engaging.
- Language Access: NCERT ensures that textbooks are accessible to students from different linguistic backgrounds, helping them learn comfortably in their native language.
Teaching Material:
NCERT develops a range of teaching materials to help teachers provide effective instruction. These materials include teacher guides, supplementary resources and digital tools. The major aspects of NCERT teaching material include:
- Pedagogical Support: Teacher guides provide valuable insight into effective teaching strategies, classroom management, and student engagement techniques.
- Supplementary Resources: NCERT provides additional resources such as workbooks, exercise sheets and reference materials to reinforce learning and cater to different learning styles.
- Digital Initiatives: In the digital era, NCERT has introduced digital resources, online modules and e-learning platforms to enhance the teaching and learning experiences.
.
Collaborations, Partnerships, and Outreach

NCERT’s collaborations with other educational bodies
The National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) in India is actively engaged in collaboration with various educational bodies, institutions and international organizations to enhance the quality of education and promote educational research and development. These partnerships are aimed at innovation, exchange of knowledge and sharing of best practices in education.
NCERT has established partnerships with other national educational bodies within India, such as the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) and the National Institute of Educational Planning and Administration (NIEPA), to develop curriculum frameworks, educational resources and research initiatives. These collaborations contribute to the continuous improvement of the Indian education system.
At the international level, NCERT collaborates with organizations such as UNESCO, UNICEF and the World Bank to address global educational challenges, share expertise and implement projects that focus on improving access to quality education, especially in disadvantaged areas. Let’s focus. These collaborations often involve joint research, capacity-building workshops, and the development of educational materials.
In addition, NCERT associates with foreign universities and institutions to promote academic exchange, collaborative research and sharing of academic perspectives. These partnerships enable integration of diverse perspectives and innovative ideas in the Indian education landscape.
In conclusion, NCERT’s collaboration with various educational bodies, institutions and international organizations plays a significant role in shaping educational policies, curriculum development, research initiatives and overall improvement of education in India as well as contributing to global education initiatives.
NCERT’s efforts to disseminate educational resources (both online and offline)
NCERT has made significant strides in dissemination of educational resources through both online and offline channels, ensuring that its valuable content reaches a diverse and wide audience:
- Online Platforms: NCERT has launched digital platforms such as e-Pathshala and DIKSHA, which provide a vast repository of e-books, interactive modules, videos and teaching aids. These platforms provide easy access to learning material for students, teachers and parents.
- Digital Textbooks: NCERT offers digital versions of its textbooks, making them available to students on computers, tablets and smartphones.
- Video Lectures: NCERT produces video lectures on various subjects, which are accessible through its online platform and video-sharing platforms. These lectures enable visual and auditory learning while meeting different learning preferences.
- Mobile Apps: Mobile Apps of NCERT provide interactive learning experience, quizzes and study materials. These apps take advantage of the popularity of smartphones to make learning engaging and accessible.
- Online Teacher Training: NCERT conducts online workshops and training programs for teachers through webinars and virtual platforms. This ensures that professional development reaches teachers from all walks of life.
- Offline distribution: NCERT continues to distribute physical textbooks in schools, especially in areas with limited digital infrastructure. It ensures that quality educational resources are accessible despite technical barriers.
- Radio and Television: NCERT collaborates with radio and television channels to broadcast educational content, reaching students in remote areas where digital access may be limited.
- Collaboration: NCERT partners with state educational boards, institutions and NGOs to enhance the reach of its resources. These collaborations facilitate the distribution of materials through local networks.
NCERT’s joint efforts in disseminating online and offline resources demonstrate its commitment to equity and inclusiveness, ensuring that quality education transcends geographical, technological and socio-economic barriers.
Challenges and Future Prospects:

Challenges or criticisms faced during its journey
While the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) has played a significant role in shaping education in India, it has not been without its challenges and criticisms. The notable challenges and criticisms faced by NCERT throughout its journey include:
- Curriculum overload: One criticism is that the NCERT curriculum framework can be overly broad and overwhelming for students. Balancing the need for comprehensive content with the risk of excessive burden on students has been a challenge.
- Inflexibility: Critics argue that standardized curricula may lack the flexibility to meet individual student interests, diverse learning styles, and local contexts. Striking a balance between the national framework and local education remains a challenge.
- Outdated material: In some cases, NCERT textbooks and resources have been criticized for not keeping pace with rapidly changing information and technological advancements. Ensuring that content remains relevant and current is an ongoing challenge.
- Linguistic Diversity: India’s linguistic diversity poses challenges in translation and adaptation of educational resources in various regional languages. Ensuring accuracy, consistency and cultural relevance in translation can be complex.
- Teacher training access: Despite efforts, accessing training and professional development opportunities for all teachers remains challenging, especially in remote areas with limited infrastructure and resources.
- Technology Gap: While NCERT has embraced digital initiatives, the digital divide in India poses challenges. Ensuring that online resources are accessible to all, regardless of socio-economic background and technical infrastructure, is a concern.
- Pressure of assessment: Critics argue that the NCERT’s emphasis on assessment and examinations may contribute to a culture of rote learning. Balancing assessment with promoting critical thinking and conceptual understanding is an ongoing challenge.
- Equity and Inclusion: While NCERT strives for inclusiveness, critics highlight that some marginalized communities may still face barriers to quality education. It is important to address these inequalities and ensure equal access to resources.
- Resistance to Change: Implementing a new educational approach or curriculum change may face resistance from various stakeholders including teachers, parents and policy makers. Managing this resistance while developing education methods is a challenge.
- Political interference: Sometimes, political factors can influence educational policies and decisions, which can potentially affect the autonomy of educational institutions like NCERT.
It is important to note that while these challenges and criticisms exist, NCERT has also demonstrated adaptability and commitment to address them. As education continues to evolve, NCERT’s response to these challenges contributes to its continued growth and relevance in shaping India’s education system.
Future Directions of NCERT
the future directions of NCERT are likely to revolve around technology integration, personalized learning, skill development, global awareness and continuous efforts towards inclusive and innovative education. Adapting to the changing educational scenario and societal needs, NCERT is set to play a significant role in shaping India’s education system in the years to come.
- Digital integration: NCERT is likely to adopt technology more, creating interactive digital content, mobile apps and virtual learning environments to meet the needs of the tech-savvy generation.
- Personalized learning: Organizations can explore personalized learning paths, leveraging AI and data analytics to customize content based on individual student progress and learning preferences.
- Skill development: As the demand for practical skills increases, NCERT may focus on integrating more skill-based and vocational education components in its curriculum.
- Global Education: With the world becoming more interconnected, NCERT can emphasize a global perspective in its resources, promote cultural understanding and prepare students for a global world.
- Inclusivity and Diversity: NCERT is likely to continue its efforts for inclusive education, ensuring that resources are accessible to students with disabilities and diverse cultural backgrounds.
- Environmental Awareness: In view of the increasing importance of environmental issues, NCERT may integrate sustainability education in all subjects, raising awareness about ecological challenges and solutions.
- Blended Learning: NCERT may adopt a blended learning approach by combining online and offline resources to provide a flexible and effective learning experience to suit different environments
- Teacher Professional Development: The organization may expand its online teacher training initiative, providing teachers with continuous professional development to enhance teaching quality.
- Curriculum flexibility: NCERT may explore more flexible curriculum models, allowing teachers and schools to adapt content to local contexts while maintaining core learning objectives.
- Assessment Reforms: In response to the evolving learning patterns, NCERT may develop alternative assessment methods that focus on holistic learning, critical thinking and real-world application.
- Research-based practices: The NCERT is likely to continue its commitment to evidence-based educational practices, conducting research that informs innovative teaching methods and educational policies.
- Collaboration: Collaborating with international educational institutions and organizations will enable NCERT to exchange ideas, resources and best practices, thereby enriching its approach towards education.
Conclusion

The National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) is an apex educational organization in India, focused on shaping the education landscape through its wide range of initiatives. Established in 1961, the historical journey of NCERT can be traced back to Dr. D.S. marked by visionary personalities like Kothari and Professor Yashpal as well as landmark initiatives like the Kothari Commission. The influence of NCERT is spread through curriculum framework, textbooks and learning materials which give priority to holistic learning, conceptual clarity and inclusivity.
These resources have standardized curriculum, empowered teachers, and fostered critical thinking. NCERT’s efforts extend to online platforms, digital textbooks, video lectures and collaboration for wider reach. Challenges like curriculum balance, technology gap and equity are met with adaptability. In the future, NCERT is set to embrace digital innovations, personalized learning, skill integration and global awareness while continuing its research-based, inclusive approach to education, thus continuing to be a key driver of India’s educational progress.
NCERT stands as an important pillar in shaping education by supporting research-based educational approach. Through its curriculum framework, textbooks and teaching materials, NCERT not only imparts knowledge but also inculcates critical thinking, creativity and holistic development in the students. By emphasizing conceptual understanding rather than rote memorization, NCERT resources foster a deeper connection with the subjects and encourage active engagement.
NCERT’s commitment to research-driven methodologies transforms classrooms into dynamic learning spaces. By conducting educational research, NCERT continuously refines teaching techniques, informs policy decisions, and aligns education with emerging societal needs. This emphasis on research-based pedagogy equips teachers with innovative strategies, enhances the quality of education, and empowers students with analytical skills to navigate an ever-changing world. Thus, NCERT plays an essential role in fostering a culture of learning beyond textbooks, fostering lifelong curiosity and inculcating the skills required for success in a knowledge-driven society.
In short, the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) holds significance in the education landscape by acting as a driving force for educational excellence, equity and innovation. Its contribution affects the overall development of students, teachers, educational institutions and the education sector
